For those of you who missed last week’s ISRI 2020 Market Forecast webinar, here’s a recap of the four main sections of the forecast: the economic outlook; business climate; commodity forecasts; and scrap trends and outlook.
Economic Outlook
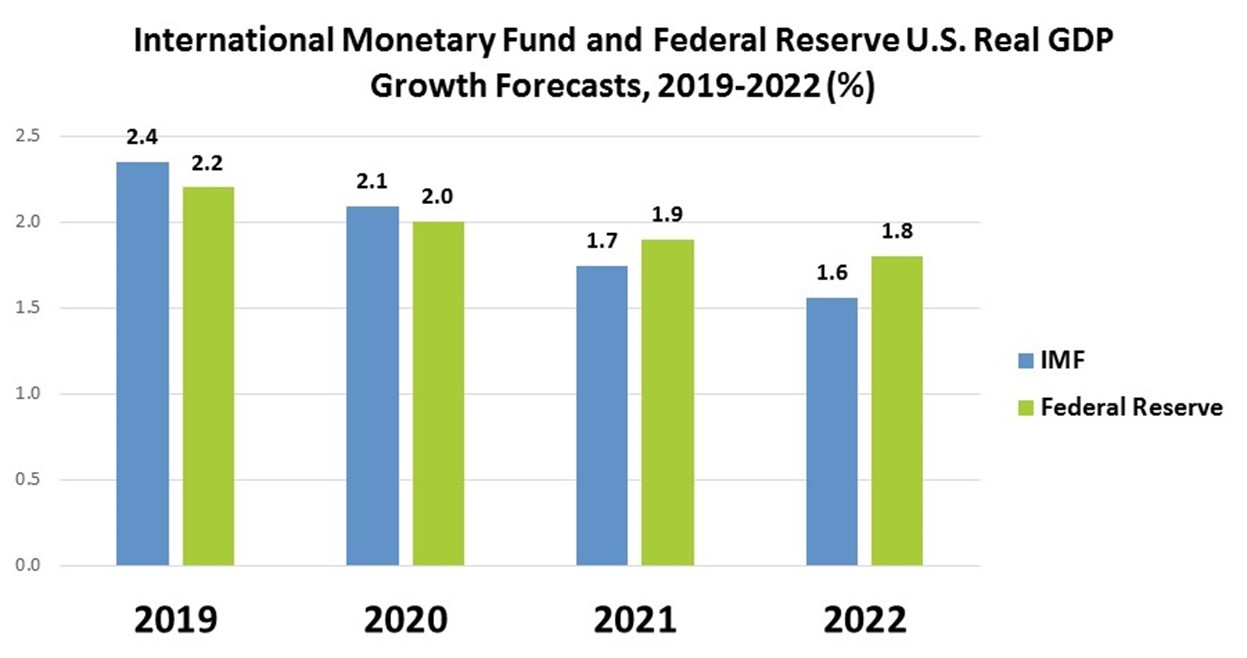
Economic growth in the United States is widely expected to slow next year, with the International Monetary Fund and Federal Reserve projecting real U.S. GDP will grow 2.1% and 2.0%, respectively, next year followed by even slower growth in 2021 and 2022.
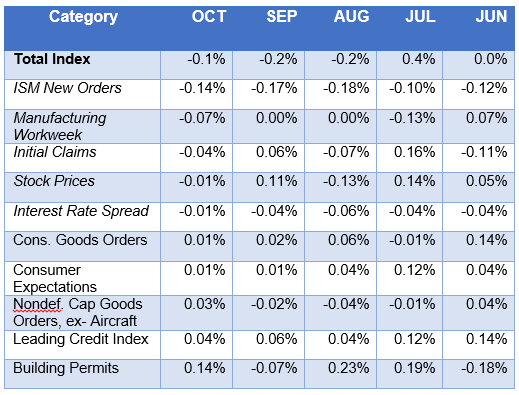
The Conference Board’s index of leading economic indicators has declined in each of the last three months, which would seem to provide additional support for expectations of slower growth ahead.
Source: The Conference Board
But the IMF sees global economic growth accelerating from 3.0% growth in 2019 to 3.4% growth in 2020 thanks to faster growth in emerging markets and developing economies. As compared to 3.9% growth in 2019, emerging markets and developing economies are projected to grow 4.6% next year, outstripping 1.7% growth in the advanced economies.
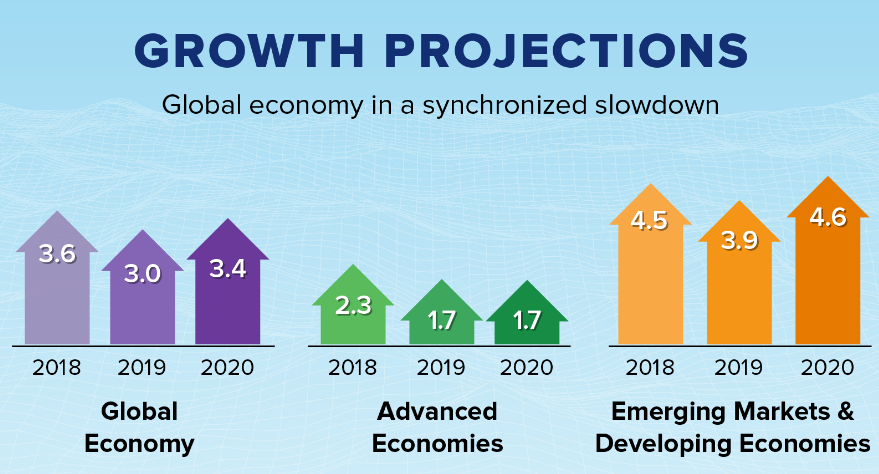
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook, October 2019.
Emerging markets and developing economies in Asia are expected to exhibit particularly strong growth next year, with the IMF projecting real GDP growth of 7.4% in Bangladesh, 7.0% in India, 6.5% in Vietnam, 6.2% in the Philippines, 5.1% in Indonesia, and 4.4% in Malaysia, making next year’s ISRI trade mission to SE Asia particularly timely.

Business Climate
A major concern for the U.S. economy is the apparent downturn in business sentiment and accompanying weakness in business investment. According to the latest figures from the Bureau of Economic Analysis, gross private domestic investment in the United States declined 6.3% in the second quarter and slipped 0.1% in the third quarter of 2019. The Business Roundtable’s CEO survey also indicates softening business sector sentiment:
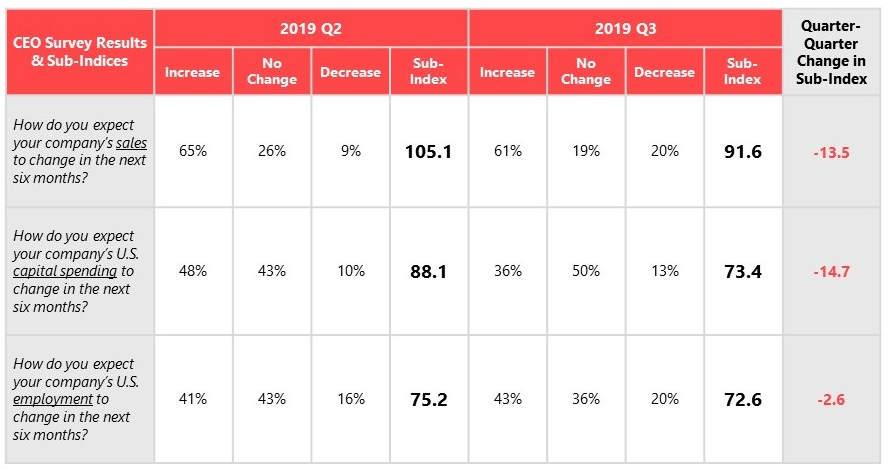
In addition, IHS Markit reports that U.S. business optimism has hit a 3-year low: “The latest IHS Markit Business Outlook survey signals that U.S. private sector firms are less optimistic towards the outlook for business activity over the coming 12 months than in June. The net balance of firms expecting a rise in output has dropped from +16% in June to +10% in October and is the lowest for three years. The net balance of firms forecasting growth is also below the global (+14%) and developed market (+12%) averages. Both manufacturing and service sector firms expressed a lower level of positive sentiment towards future output than earlier in the year.”
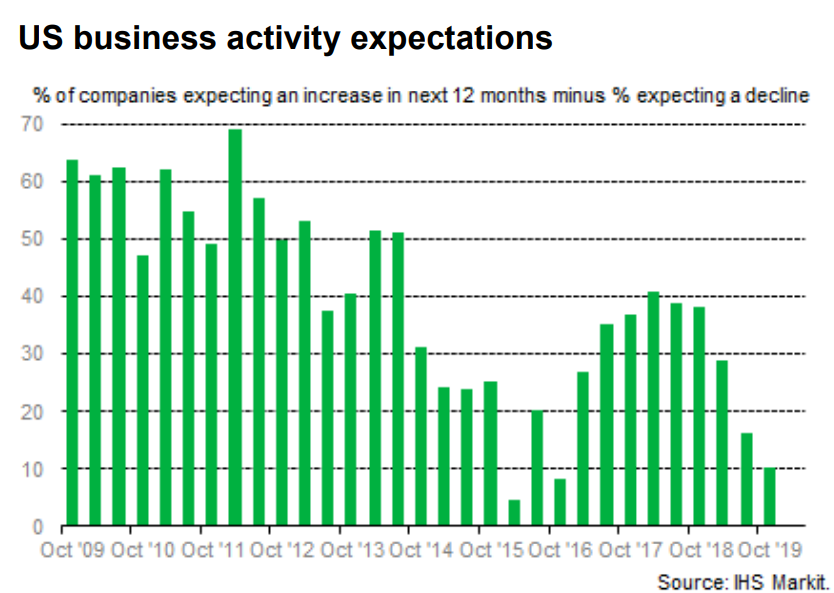
Commodity Forecasts
In contrast to business sentiment, global metal market sentiment has shown some signs of improvement lately. According to IHS Markit:
- “Ending a 12-month sequence of contraction, the volume of new orders at global steel users increased solidly during October… this was concentrated on Asian companies, and related to stronger market demand.
- Asian businesses reported the strongest rise in {copper} demand in over a year-and-a-half, whereas new order growth at US firms slowed to an eight-month low. The decline in new orders at European firms meanwhile extended to a whole year.
- Aluminum users raised output levels sharply at the start of the fourth quarter, with the rate of expansion accelerating notably from the previous month. Surveyed companies related this to an uplift in new orders that followed 12 successive months of decline.”
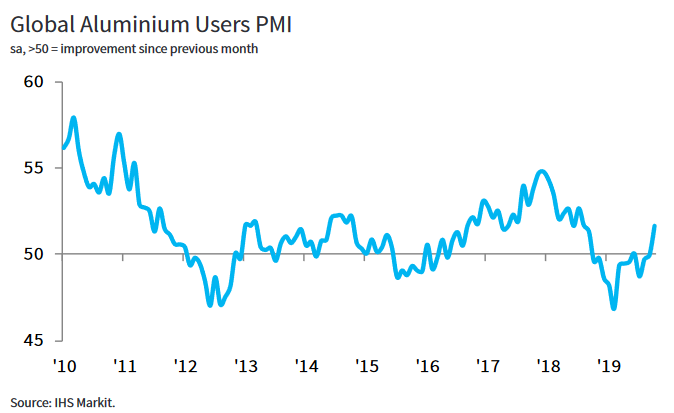
Turning to the paper and fiber markets, recent RISI Viewpoints report on the continued impact of China’s recovered paper import restrictions on the global pulp, virgin, and recovered paper markets:
- “There is a “massive” amount of inventory in market pulp globally, and reaching a market balance won’t occur until the inventory is reduced, according to Fastmarkets RISI’s VP of Fiber Dave Fortin. He added that economic softening in the US and globally next year also could slow the inventory drawdown. And with the uncertainty about the US/China trade war, Fortin told attendees at Fastmarkets RISI’s North American Forest Products Conference in Boston on Oct. 29 that “we think market pulp could remain weaker longer... The rebalancing can’t happen until (there are) significant capacity curtailments.”
- Recycled pulp has become an alternative way for Chinese paper producers to obtain the recycled fiber they need. Chinese recycled pulp imports jumped sharply by 205% year-over-year to about 460,000 tonnes in the first eight months of this year. Chinese paper companies have plans to invest in significant amounts of recycled pulp capacity to expand recycled pulp production in different regions, mainly the US and non-China Asia, to solve the potential fiber shortage problem caused by the further drop in RCP imports and the potential zero-RCP-imports scenario sometime in the future.
- But when and where these recycled pulp projects will come on line will inevitably be impacted by China’s fundamental demand for recycled fiber, China’s regulations on recycled pulp imports and regulations in the countries and regions where the recycled pulp projects are planned. The trade tension between the US and China will add some uncertainty to Chinese paper companies’ recycled pulp plans as well.”
As for the outlook for energy markets, the U.S. Energy Information Administration reports “U.S. commercial crude oil and other liquids inventories declined by 0.4 million barrels per day(b/d) in October. EIA estimates that global inventories increased by 0.8 million b/d in October as inventory builds in other regions—some of which was likely the result of Saudi Arabia refilling stocks that it withdrew following the September production outage—offset the draws in the United States. EIA forecasts that fourth-quarter 2019 inventories will increase by more than 0.2 million b/d, followed by further inventory builds in the first half of 2020 that will put moderate downward pressure on crude oil prices. EIA’s price forecast for 2020 is mostly unchanged from the October STEO; Brent and WTI are forecast to average $60/b and $55/b, respectively.”
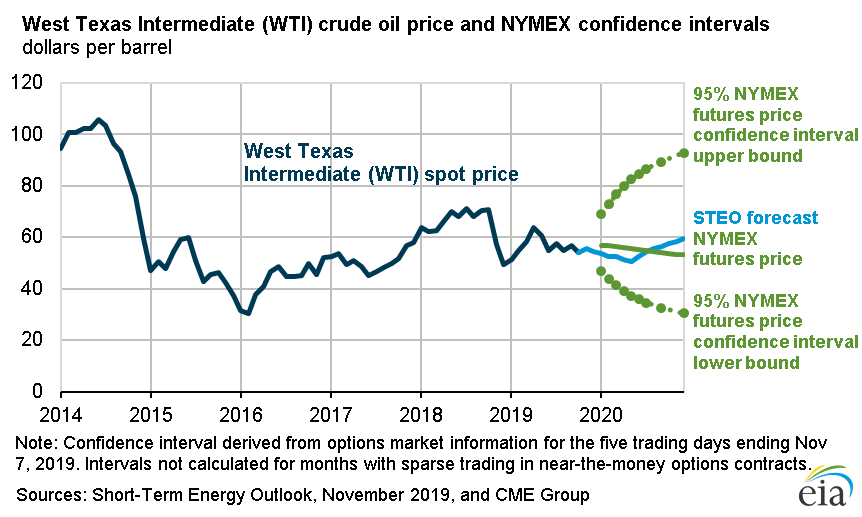
Here are the most recent metals and minerals, precious metals, and energy price forecasts from the World Bank (updated October 29, 2019):
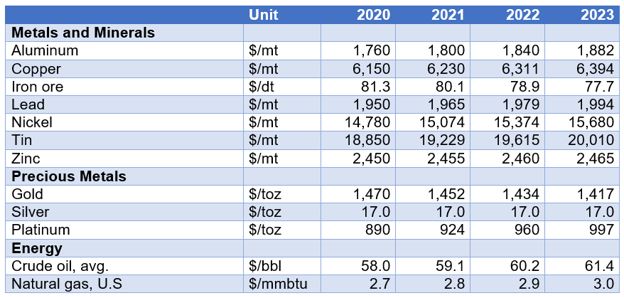
Scrap Trends and Outlook
Scrap prices across the commodities spectrum came under pressure over the course of 2019 amid signs of slower domestic manufacturing output, lackluster primary commodity price trends, reduced Chinese scrap imports, and uncertainty in the business community regarding the U.S.-China trade war, tight labor market conditions, and other risk factors.
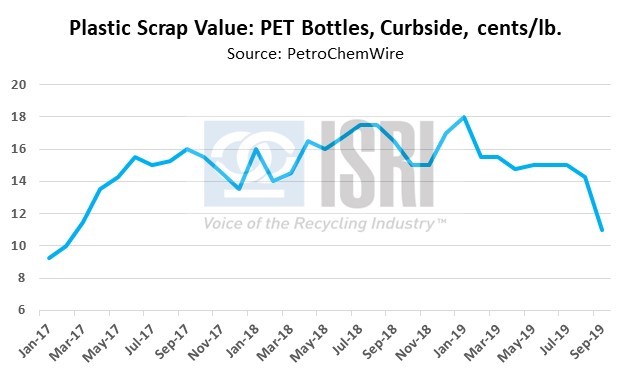
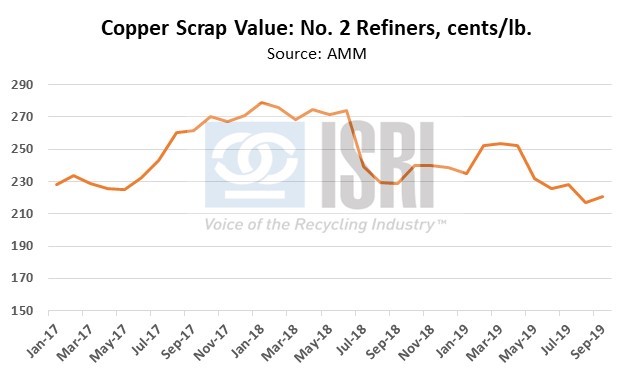
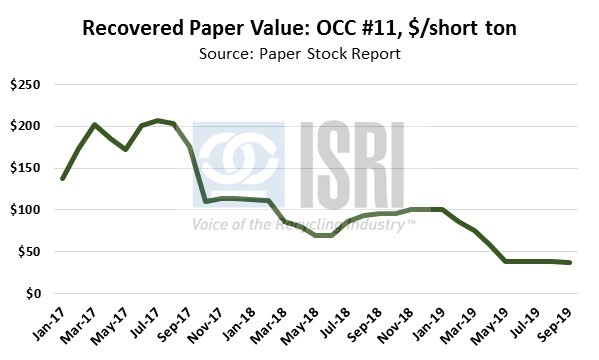
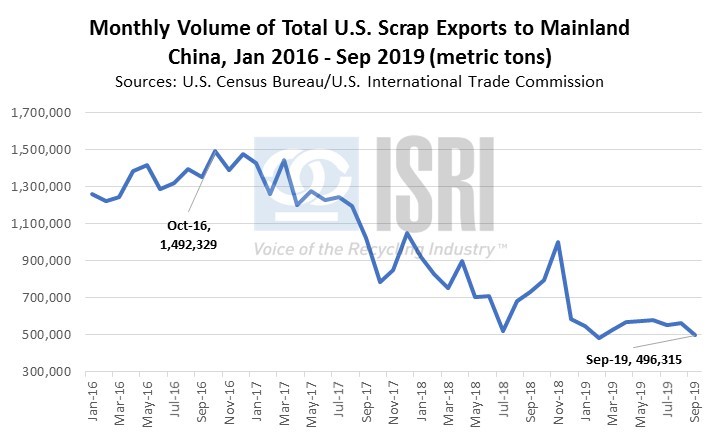
On the export front, the latest trade figures from the Census Bureau show total U.S. scrap exports (including ferrous scrap, nonferrous scrap, plastic scrap, recovered paper and fiber, and other recycled commodities) during Jan-Sep 2019 totaled 29.2 million metric tons, down 2.5% as compared to the corresponding period in 2018. By dollar value, year-to-date U.S. scrap exports are down 5% to $14.5 billion through September, a loss of nearly $785 million as compared to the first nine months of 2018. By major commodity group and dollar value, year-to-date:
- Plastic scrap exports are down 41% to $212 million;
- Ferrous scrap (ex- stainless and alloy steel scrap) exports are down 12% to $3.58 billion;
- Recovered paper and fiber exports are down 6% to $2.2 billion; and
- Nonferrous scrap (including precious metal scrap) exports are down less than 1% at $7.8 billion.
Major Themes for 2020
- Slower U.S. economic growth is expected, but rising growth in emerging and developing economies in Asia.
- Election year politics could influence economic policy, but the Federal Reserve is expected to hold on additional rate cuts early in the year.
- Business optimism in the United States is softening as stimulus wears off, but corporate profitability has held up relatively well.
- There have been mixed readings on U.S. manufacturing, which is closely related to scrap demand, although there are continued capacity expansion plans.
- Commodity market sentiment appears to be improving but price forecasts are lukewarm.
- China will continue to impact the global scrap marketplace in 2020 as Beijing revisits how scrap imports are categorized even as U.S./North American demand takes on a larger role.
- Transportation issues including for barges, rail, truck, and containers are still seen as difficult.
- Rising public awareness about sustainable development will continue to shape perceptions about recycling.
- Focus on QUALITY and consistency to meet consumer demands at home and abroad has become the key.
- Recyclers are increasingly focused on (new and end) market development and the targeted investments required to produce high-quality recycled commodities.
- Recycling is a shared responsibility that requires collaboration across the private and public sectors.